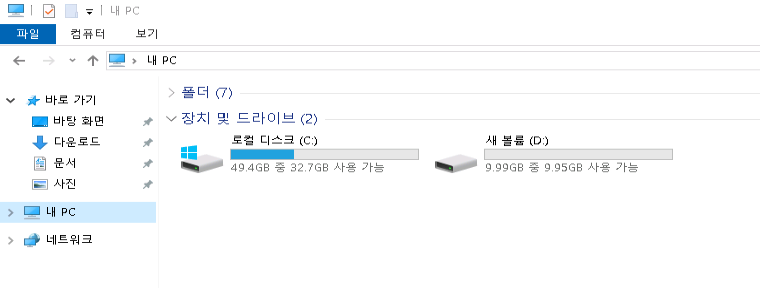
블록 스토리지 포맷 및 마운트
블록스토리지를 Linux/Windows 가상서버에 연결(마운트) 하는 방법을 단계별로 안내합니다.
본 메뉴얼은 사용중인 서버 운영체제별로 하단 탭을 선택한 후 확인하실 수 있는 가이드입니다.
- Linux
- Windows
1. 블록 스토리지 장착 여부 확인
먼저 서버에서 블록스토리지가 연결되어 있는지 확인합니다.
[root@iwinvtest ~]# fdisk -l
출력 예시는 다음과 같습니다.
OS 디스크
Disk /dev/vda: 26.8 GB, 26843545600 bytes
139 heads, 8 sectors/track, 47148 cylinders
...
/dev/vda1 2 47149 26213376 83 Linux
블록 스토리지 디스크
Disk /dev/vdb: 10.7 GB, 10737418240 bytes
16 heads, 63 sectors/track, 20805 cylinders
...
Disk identifier: 0x00000000
2. 블록 스토리지 파티션 설정
디스크 용량에 따라 블록스토리 파티션 설정 시 도구가 다르기 때문에 이에 맞��춰 설정하도록 합니다.
| 디스크 용량 | 파티션 도구 | 비고 |
|---|---|---|
| 2TB 이하 | fdisk | MBR 방식 지원 |
| 2TB 초과 | parted | GPT 방식 필수 |
fdisk로 파티션 설정할 경우
디스크 용량이 2TB 이하 일경우 fdisk로 파티션을 설정하도록 합니다.
[root@iwinvtest ~]# fdisk /dev/vdb
실행 중 입력 순서는 다음과 같습니다.
Command (m for help): n (입력)
Command action
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
p (입력)
Partition number (1-4): 1 (입력)
First cylinder (1-20805, default 1): (엔터입력)
Using default value 1
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (1-20805, default 20805): (엔터입력)
Using default value 20805
Command (m for help): wq (입력)
wq 입력 시 파티션 정보가 저장되고, 디스크 테이블이 갱신됩니다.
parted로 파티션 설정할 경우
디스크 용량이 2TB 초과 일경우 parted로 파티션을 설정하도록 합니다.
[root@iwinvtest ~]# parted /dev/vdb
실행중 입력 순서는 다음과 같습니다.
GNU Parted 3.2
Using /dev/vdb
Welcome to GNU Parted! Type 'help' to view a list of commands.
(parted) mklabel gpt # GPT 파티션 테이블 생성
(parted) mkpart primary ext4 0% 100% # 전체 영역 1개 파티션
(parted) print # 파티션 확인
(parted) quit
3. 블록 스토리지 포맷
생성된 파티션(/dev/vdb1)을 ext4 파일시스템으로 포맷합니다.
[root@iwinvtest ~]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/vdb1
mkfs.ext4 : ext4 포맷으로 새 파일시스템을 생성합니다.
출력 마지막에 다음과 같은 문구가 표시되면 정상 완료 입니다.
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal: done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
4. UUID 확인
마운트 시 UUID를 사용하는 것이 안전합니다.
[root@iwinvtest ~]# blkid
출력 예시는 다음과 같습니다.
/dev/vda1: UUID="8328eca5-aa6e-4820-80d9-373ed1627d7c" TYPE="ext4"
/dev/vdb1: UUID="fd68aff1-0dd4-42d2-8ef9-6d6dd1814df1" TYPE="ext4"
5. 블록 스토리지 마운트
이제 /mnt 디렉터리에 블록스�토리지를 마운트합니다.
[root@iwinvtest ~]# mount UUID="fd68aff1-0dd4-42d2-8ef9-6d6dd1814df1" /mnt
다음과 같이 명령어를 입력하였다면, /mnt경로 아래에 디스크 공간이 연결됩니다.
6. 마운트 확인
마지막으로 마운트가 정상적으로 되었는지 확인합니다.
[root@iwinvtest ~]# df -Th
출력 예시는 다음과 같습니다.
Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/vda1 ext4 25G 643M 23G 3% /
/dev/vdb1 ext4 9.8G 23M 9.2G 1% /mnt (마운트 성공)
/dev/vdb1이 /mnt에 표시되면 마운트가 성공입니다.
리부팅 후에도 해당 마운트를 유지할 경우 /etc/fstab에 UUID를 등록해두는 것을 권장드립니다.
CF. 블록스토리지 파티션 분할하여 사용하기
블록스토리지의 경우 물리적으로 분할 하는 것은 불가능하지만 블록스토리지의 파티션을 분할하여 논리적으로 나누어 사용하는 것은 가능합니다. 만약 신청하신 블록스토리지 용량이 크다면 파티션을 분할하여 원하는 목적에 맞게 사용할 수 있습니다.
예를 들어 1TB 짜리 블록스토리지를 신청한 후 600GB와 400GB로 나누어서 목적에 맞게 할당할 수 있습니다.
1. 블록스토리지 장치명 확인
1TB짜리 블록스토리지를 생성한 후 fdisk로 확인했을때 /dev/vdb가 생성된 ��것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
root@iwinvtest:~# fdisk -l
Disk /dev/vda: 25 GiB, 26843545600 bytes, 52428800 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: gpt
Disk identifier: EA4ABF59-D802-467D-8B53-F851754FDA36
Device Start End Sectors Size Type
/dev/vda1 2099200 52428766 50329567 24G Linux filesystem
/dev/vda14 2048 10239 8192 4M BIOS boot
/dev/vda15 10240 227327 217088 106M EFI System
/dev/vda16 227328 2097152 1869825 913M Linux extended boot
Partition table entries are not in disk order.
Disk /dev/vdb: 1000 GiB, 1073741824000 bytes, 2097152000 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x15caf035
2. 파티션 할당
하나의 장치는 600GB로 다른 하나의 장치는 399GB로 할당해줍니다.
root@iwinvtest:~# fdisk /dev/vdb
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.39.3).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/vdb: 1000 GiB, 1073741824000 bytes, 2097152000 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x15caf035
Command (m for help): n
Partition type
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended (container for logical partitions)
Select (default p): p
Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1
First sector (2048-2097151999, default 2048):
Last sector, +/-sectors or +/-size{K,M,G,T,P} (2048-2097151999, default 2097151999): +600G
Created a new partition 1 of type 'Linux' and of size 600 GiB.
Command (m for help): n
Partition type
p primary (1 primary, 0 extended, 3 free)
e extended (container for logical partitions)
Select (default p): p
Partition number (2-4, default 2): 2
First sector (1258293248-2097151999, default 1258293248):
Last sector, +/-sectors or +/-size{K,M,G,T,P} (1258293248-2097151999, default 2097151999): +400G (디스크 끝의 여유공간이 필요하기에 여기서는 400GB 할당이 되지 않습니다.)
Value out of range.
Last sector, +/-sectors or +/-size{K,M,G,T,P} (1258293248-2097151999, default 2097151999): +399G
Created a new partition 2 of type 'Linux' and of size 399 GiB.
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered.
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
3. 파티션 확인
할당된 장치 /dev/vdb1, /dev/vdb2를 확인할 수 있습니다.
root@iwinvtest:~# fdisk /dev/vdb
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.39.3).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/vdb: 1000 GiB, 1073741824000 bytes, 2097152000 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x15caf035
Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type
/dev/vdb1 2048 1258293247 1258291200 600G 83 Linux
/dev/vdb2 1258293248 2095056895 836763648 399G 83 Linux
4. 파일시스템 포맷
파일시스템을 포맷해줍니다.
root@iwinvtest:~# mkfs.ext4 /dev/vdb1
mke2fs 1.47.0 (5-Feb-2023)
Creating filesystem with 157286400 4k blocks and 39321600 inodes
Filesystem UUID: ad3829bb-ef2e-4b6e-94c6-72ef91cf8178
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632, 2654208,
4096000, 7962624, 11239424, 20480000, 23887872, 71663616, 78675968,
102400000
Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (262144 blocks):
done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
root@iwinvtest:~# mkfs.ext4 /dev/vdb2
mke2fs 1.47.0 (5-Feb-2023)
Creating filesystem with 104595456 4k blocks and 26148864 inodes
Filesystem UUID: 3ea0ac05-8db9-46fe-9ce7-0f907ff7b85b
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632, 2654208,
4096000, 7962624, 11239424, 20480000, 23887872, 71663616, 78675968,
102400000
Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (262144 blocks): done
Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done
5. blkid를 통해 파일시스템 포맷을 한 장치의 UUID 값 확인
위에서 파일시스템 포맷을 진행한 /dev/vdb1과 /dev/vdb2 장치의 UUID값을 확인합니다.
root@iwinvtest:~# blkid
/dev/vda15: LABEL_FATBOOT="UEFI" LABEL="UEFI" UUID="3D2E-C65D" BLOCK_SIZE="512" TYPE="vfat" PARTUUID="cd261615-18d7-4d4d-bec6-bd2bfecdf6d7"
/dev/vda1: LABEL="cloudimg-rootfs" UUID="8bd862e8-c4b6-4741-b54e-45b3ef5af4c7" BLOCK_SIZE="4096" TYPE="ext4" PARTUUID="ab79d57d-8d37-48ed-8213-fd1a7c6263e9"
/dev/vda16: LABEL="BOOT" UUID="400db5ab-552d-4ff6-becb-013a32d30ddc" BLOCK_SIZE="4096" TYPE="ext4" PARTUUID="d6212785-4c37-426a-956f-73dd5d4313fd"
/dev/vdb2: UUID="3ea0ac05-8db9-46fe-9ce7-0f907ff7b85b" BLOCK_SIZE="4096" TYPE="ext4" PARTUUID="15caf035-02"
/dev/vdb1: UUID="ad3829bb-ef2e-4b6e-94c6-72ef91cf8178" BLOCK_SIZE="4096" TYPE="ext4" PARTUUID="15caf035-01"
/dev/vda14: PARTUUID="b3663984-a1ad-408a-8211-abca48e85e6a"
6. 목적대로 사용할 임의의 폴더 2개 생성
목적에 맞게 폴더를 생성해줍니다.
root@iwinvtest:/home# mkdir test1
root@iwinvtest:/home# mkdir test2
root@iwinvtest:/home# ll
total 20
drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 Oct 17 15:47 ./
drwxr-xr-x 22 root root 4096 Oct 17 15:54 ../
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Oct 27 09:24 test1/
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Oct 27 09:25 test2/
7. 위에서 확인한 UUID 값 넣어준다.
blkid를 통해 확인한 블록스토리지 장치의 UUID 값을 /etc/fstab에 넣어줍니다. /etc/fstab에 넣어주어야 부팅 후에도 장치의 연속성을 유지할 수 있습니다.
root@iwinvtest:~# vi /etc/fstab
LABEL=cloudimg-rootfs / ext4 discard,commit=30,errors=remount-ro 0 1
LABEL=BOOT /boot ext4 defaults 0 2
LABEL=UEFI /boot/efi vfat umask=0077 0 1
LABEL=ad3829bb-ef2e-4b6e-94c6-72ef91cf8178 /home/test1 ext4 defaults 0 2
LABEL=3ea0ac05-8db9-46fe-9ce7-0f907ff7b85b /home/test2 ext4 defaults 0 2
8. 마운트 작업
장치의 목적에 따라 마운트 진행합니다.
root@iwinvtest:~# mount /dev/vdb1 /home/test1
root@iwinvtest:~# mount /dev/vdb2 /home/test2
9. 할당된 파티션 확인
할당된 장치를 확인할 수 있습니다.
root@iwinvtest:~# df -TH
Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
tmpfs tmpfs 101M 1.2M 100M 2% /run
/dev/vda1 ext4 25G 3.6G 22G 15% /
tmpfs tmpfs 505M 0 505M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs tmpfs 5.3M 0 5.3M 0% /run/lock
/dev/vda16 ext4 924M 118M 741M 14% /boot
/dev/vda15 vfat 110M 6.4M 103M 6% /boot/efi
tmpfs tmpfs 101M 13k 101M 1% /run/user/0
/dev/vdb1 ext4 633G 29k 601G 1% /home/test1
/dev/vdb2 ext4 421G 29k 400G 1% /home/test2
1. 디스크 관리 실행
추가한 블록스토리지를 설정하기 위해 디스크 관리(disk Management) 창으로 진입합니다.
방법 1 - 실행창을 통해 진입
Windows 키 + R입력- 실행창에
diskmgmt.msc입력 후 Enter
직접 입력 시 바로 디스크 관리 창이 열립니다.
방법 2 - 제어판을 통해 진입
- 제어판 → 시스템 및 보안 → 관리 도구 → 컴퓨터 관리
- 좌측 메뉴에서 디스크 관리 선택
2. 블록스토리지 확인
디스크 관리 창에서 새로 추가한 10GB 블록스토리지가 디스크 1로 표시됩니다.
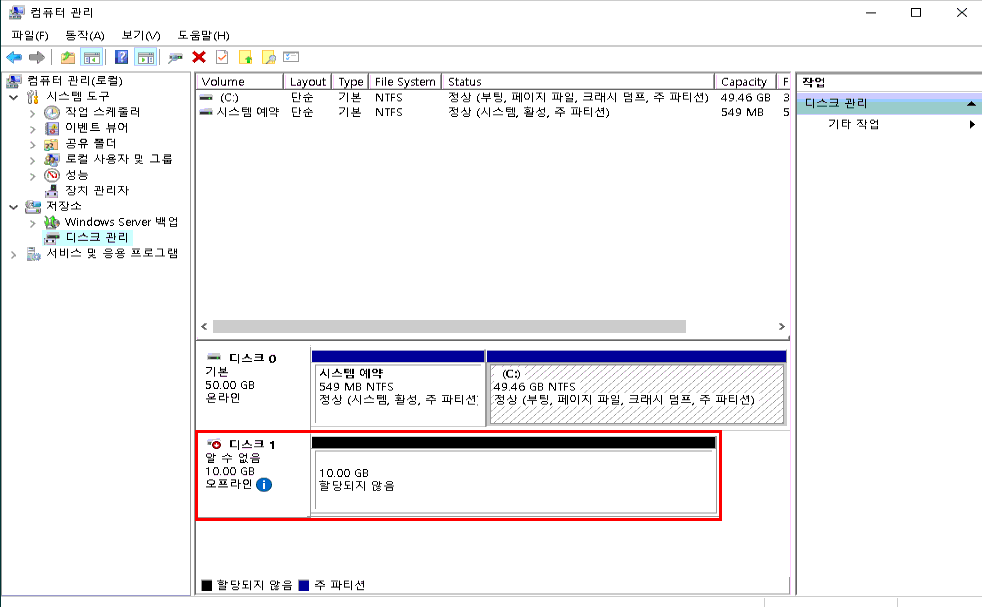
만약 디스크가 자��동으로 표시되지 않을 경우 "디스크 다시 검색"을 클릭합니다.
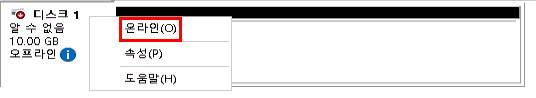
3. 디스크 상태 변경
새로 추가된 디스크는 기본적으로 오프라인 상태입니다.
디스크 1을 우클릭- 온라인으로 설정 선택
↓
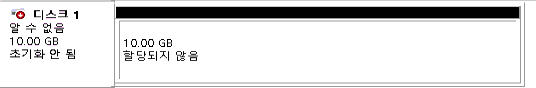
디스크가 온라인으로 변경되면 상태 표시가 회색 → 검정색으로 바뀝니다.
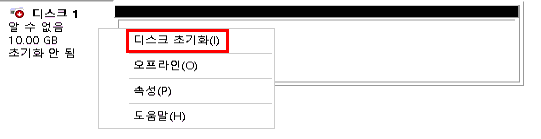
4. 디스크 초기화
이제 디스크를 사용할 수 있도록 초기화를 진행합니다.
디스크 1을 우클릭 → 디스크 초기화- 아래 두 가지 형식 중 하나를 선택
| 파티션 형식 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| MBR (Master Boot Record) | 2TB 미만 디스크에서 사용 가능. 대부분의 일반 SSD/HDD에 적합 |
| GPT (GUID Partition Table) | 2TB 이상 대용량 디스크용. 부팅 영역 없이 데이터 저장용으�로 사용 가능 |
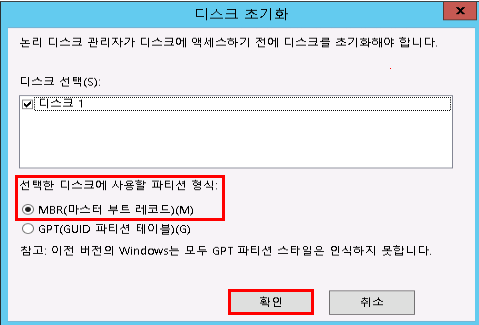
본 예제에서는 10GB SSD 블록스토리지를 사용하므로 MBR 형식으로 초기화합니다.
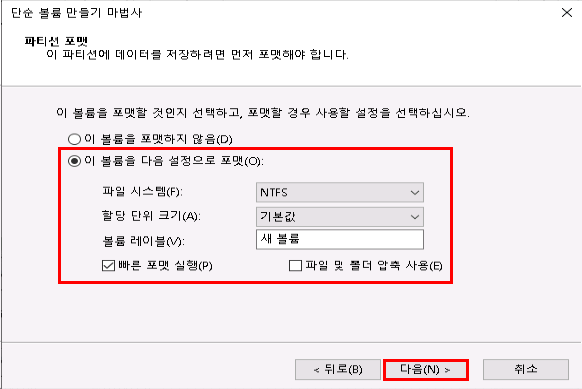
5. 새 단순 볼륨 생성
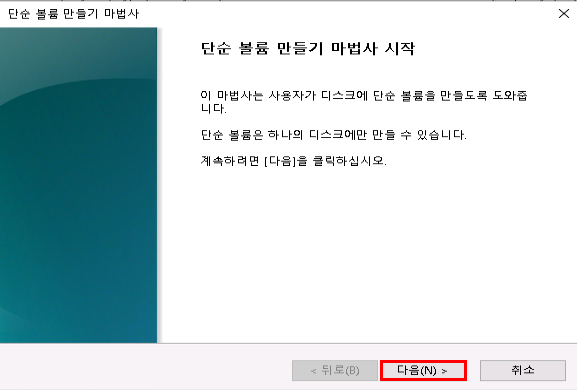
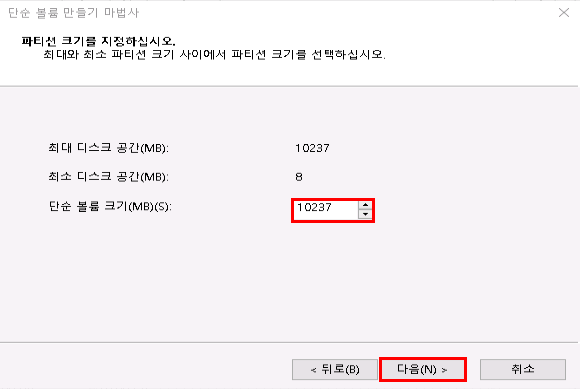
디스크 초기화가 완료되면, 파티션을 생성해야 합니다.
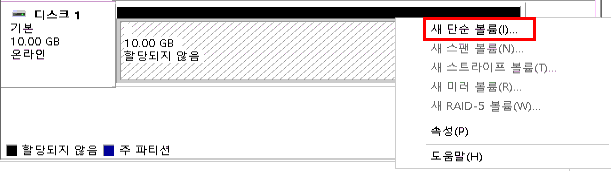
할당되지 않음영역을 우클릭 → 새 단순 볼륨(New Simple Volume) 선택- 단순 볼륨 만들기 마법사 실행됨
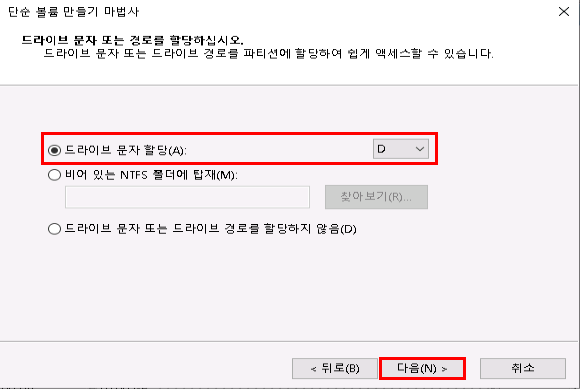
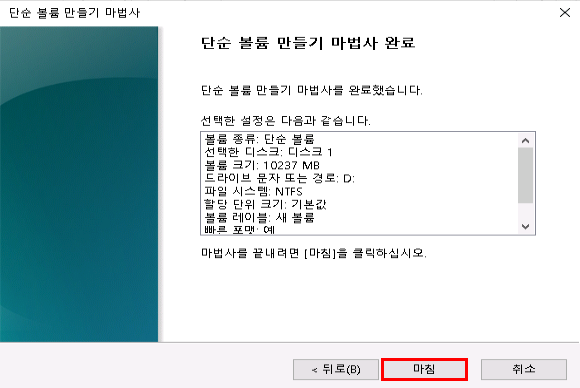
6. 마운트 완료 확인
볼륨 생성이 완료되면 새 디스크가 자동으로 마운트됩니다.